How to protect video games
This guide will show you the possibilities of legal protection of video games regardless of gaming platform. It is intended for those who are willing to market their video games or publish them by any means. Guide is however not comprehensive, as the individual issues will be discussed in future articles, but it is willing to provide an overview of your possibilities to protect your creative work.
Most of the bellow mentioned processes can be done by everyone willing to invest enough time and effort, but professional guidance of IP specialist is always advisable. Therefore this guide will be set mostly from perspective of startups or small to medium sized businesses willing to seek legal protection for their current or future digital creations.
What is a video game?
We will discuss the issue from the point of view which says that video games are defined as complex creative works consisting of multiple elements that can be protected separately like graphics, code, characters etc. However the core element of every video game is computer program – the original code that puts all these elements together into one unique creation. Thus there is no such thing in law as „registration of video game“ in some sort of register and everything is safe and protected (in comparisson to other intellectual property assets like trademarks, patents, designs etc.).
This view and definition can vary from country to country, as no country in the world has regulated this issue in detail so far, however this opinion is accepted in many countries.

What game elements can be protected?
Every video game element already created can be subject to some type of legal protection. The essential questions are:
What is the right type of IP protection for certain game elements?
How to achieve such protection?
We will try to answer these questions here. Chart bellow should help you to easily identify answers to these questions. Brief explanation can be found under the chart.
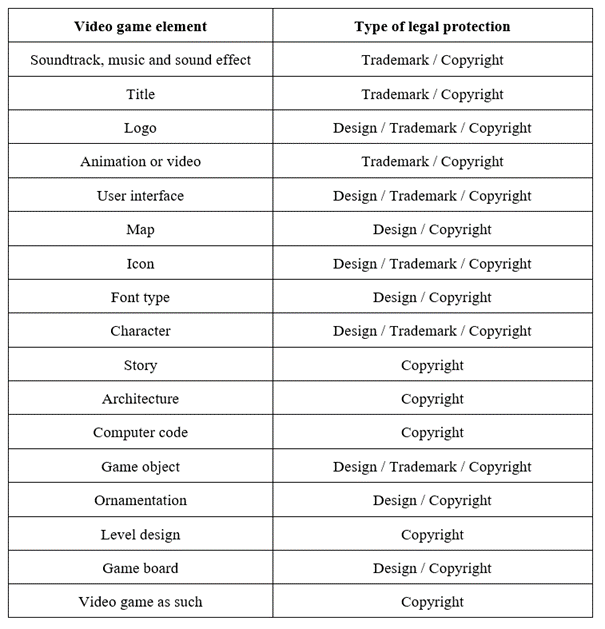
Firstly we must point out that this chart shows the most effective and most used legal protection strategy for specific game element. However it is not excluded that for instance Game board or Map can be registered also as a trademark if the law and pertinent office allows that. Details depend on pertinent game element and jurisdiction.
Copyright
As you may have noticed, all of the game elements may be protected by copyright which in most countries does not require any kind of registration. In some countries, like UK and US, you can register your copyright, however such registration has only informative character and does not mean that your rights are „created“ from this moment. This sort of registration may be used as supportive evidence when you need to prove that the certain rights existed in particular moment in the past. Such evidence can be very good to have in litigation.
Design
If you check the table above, you can see some of the game elements are good to be protected by design. It protects the novelty and individual character of shape, patterns, lines, material or ornaments of the game element. In order to register something as design, most countries requires design to be novel and have individual character. Designs can be registered in most countries of the world on national, regional and international level. We will write more on designs later on.

Trademark
While registered design can cover some aspects of legal protection of pertinent game element, trademark is must have to protect some essential aspects of your game. If it comes to for instance Logo of the game, I nearly can not imagine any serious gaming studio that has not registered their fancy logo of their game as trademark. Animated logos can be also registered as trademarks which is very neglected, but very modern way, to protect and to stand out.
Game title is the same story as game logo, as it is very important for game studio to have exclusivity on using their game title. Nobody wants someone else to use his creation title freely in business without his permission, right?
Companies are also registering distinctive game characters, icons, architectural objects and even sounds as trademarks. We can thus state that there are many various combinations and possibilities to legally protect your video game.
Why should you legally protect video game?
In current situation, in which video games are sold, shared, marketed and used on global level, you can not expect everyone to act according to rules and respect your rights to your creation adequately. Therefore you must enhance your rights by registering them and taking care of them from start. That is the reality in current globalized world.
Is it expensive?
We understand that many studios, especially startups, could have problems to find affordable legal help to protect all of their intellectual property assets, but we recomment to always at least invest in introductory legal advice and register the essential elements of your game. You can invest more in it later on. And one more thing. Registration of for instance trademark lasts 10 years, so it is mostly worth it to invest in it at start and be safe during that time than be sorry for not doing so.
There is a well known myth that legal services are very expensive, but that is not true. You can always discuss your situation with lawyer. In my practise I have not seen a single case in which we would have not met someone’s wishes once we discuss the issue. It is always the matter of deal between lawyer and you. Do not fear to ask for help. In fact legal services in most countries belong, in vast majority of cases, to the lowest expense of game studio when it comes to main expenses.
The final price of registrations and all the other matters related to legal protection of your video game will depend on various factors like country in which you seek protection, scope of protection, IP specialist you choose etc.
Conclusion
This guide is written from global perspective and some information may vary depending on jurisdiction. It is also important to say that as the video gaming industry develops even more the possibilities and instruments available to protect video games on legal level will vary in the upcoming years.
Actual „system“ of legal protection of video games is very extensive and inconsistent. Thus some authors say that the new special kind of legal protection regime shall be established for video games as these types of creations are really unique, have original characteristics and have specific features which are characteristic only for video games. We can only wait and see what future brings us and discuss it later on.






